RethinkDB 2.2: atomic changefeeds, parallel scans, improved runtime
Today, we’re pleased to announce RethinkDB 2.2 (Modern Times). Download it now!
RethinkDB 2.2 includes over 120 enhancements, significantly improves performance, memory usage and scalability, adds new ReQL commands, and ships with atomic changefeed support. Some of the major improvements in the 2.2 release include:
- Atomic changefeeds: the
changescommand now accepts an optional argument calledincludeInitial, which allows atomically reading existing data and processing new results with a single query. - Optimized fetches: the
getAllcode path has been optimized to perform a single network round trip, which results in an 8x performance improvement. - Parallel scans: fetching large amounts of sequential data from RethinkDB now scales linearly with the size of the cluster.
- Improved memory usage: memory usage on large datasets has been reduced by over 50%.
- New ReQL commands: We added a new
valuescommand, and Peter Hollows expandedr.uuidto support user defined hashes.
Atomic changefeeds
One of the most common patterns when building realtime web or mobile applications is to render the page and then update it any time there is new information. For example, if you’re presenting your users with a leaderboard, you’d typically want to render the leaderboard right away, and then update it when it changes.
Prior to RethinkDB 2.2 you could accomplish it by running two separate queries: one to fetch initial data, and another to listen to changes.
// Get the initial data for top ten players
var leaderboard = r.table('gameplays')
.filter(r.row.gt(1000))
.run(conn);
// Open a changefeeed to receive updates
var changes = r.table('gameplays')
.filter(r.row.gt(1000))
.changes()
.run(conn);
There are two problems with this approach. First, you have to write two different pieces of code: one to handle the initial data, and one to handle the changes. While this doesn’t present any insurmountable challenges, having to write code twice to process every piece of realtime data quickly becomes a significant burden in applications that heavily rely on realtime functionality.
The second problem is more serious – the code above contains a race condition. There is a small gap between the time you get the initial results and the time you subscribe to a feed, and new data might slip in between the two queries. When that happens, you end up missing the change, and your users are left with inconsistent information.
Changefeeds can use includeInitial
RethinkDB 2.2 fixes both problems by introducing an includeInitial option to
the changes command. When includeInitial is set to true, existing data is
automatically injected into the changefeed:
// Open a changefeed to receive updates, including initial data
var changes = r.table('gameplays')
.filter(r.row.gt(1000))
.changes({ includeInitial: true })
.run(conn);
The example above will give you all the players with a score greater than 1000. After it gives you the initial list, it will give you a stream of updates as the players scores change.
The availability of initial changefeed results simplifies realtime application development for many RethinkDB users, but it’s especially worth noting that this feature brings us one big step closer to accommodating the requirements of the popular Meteor framework, and paves the way for a robust Meteor integration.
Compatibility
In previous versions of RethinkDB, changefeeds automatically included initial
results for some queries (those using orderBy.limit or get) but not others,
and there was no way to control this behavior. In RethinkDB 2.2, changefeeds
only emit their initial results by default if you explicitly set
includeInitial to true, and the option is now available on all changefeeds.
Note: this is a breaking change. Please update your applications to explicitly
turn on includeInitial when you need it.
Performance improvements
In addition to atomic changefeeds, the 2.2 release brings significant performance, scalability, and memory efficiency improvements.
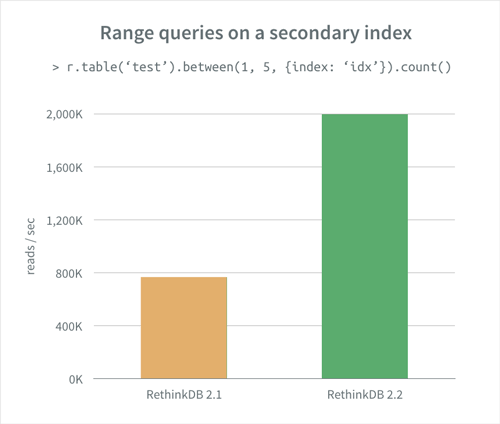
Faster secondary indexes
You can expect to see major performance gains for between
operations that rely on secondary indexes. In our internal benchmarks, a query
that uses an index to count a million items went from 1.3 seconds in RethinkDB
2.1.0 to 0.5 seconds in 2.2.
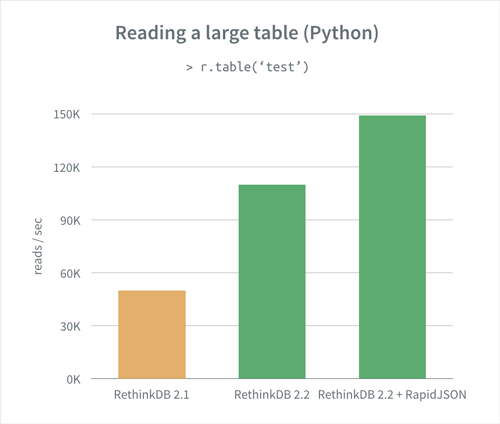
Faster streaming in Python
We also worked to deliver better performance in cases where users stream large data sets with the Python client driver. An operation that involves reading 1 million documents that are roughly 200 bytes each went from 20 seconds in version 2.1.0 to 9.1 seconds in version 2.2.
Community member Adam Grandquist contributed code that extends the Python client driver so that users can plug in third-party JSON parsing libraries like RapidJSON for faster document decoding. When we added RapidJSON to our benchmark configuration, the completion time of the million document benchmarked dropped even further, down to 6.7 seconds.
Parallel scans
The performance of fetching a large number of documents is improved even further if you’re running a RethinkDB cluster. Table scans across multiple RethinkDB servers are now done in parallel, and you can expect linear scalability on table scans as of RethinkDB 2.2.
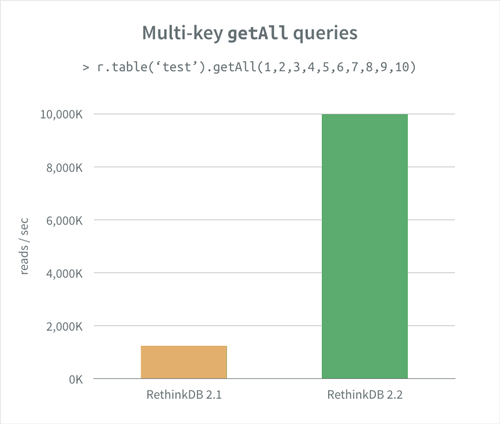
Faster getAll queries
The performance of the getAll command has also been significantly improved
since releasing RethinkDB 2.1 three months ago. If you’re using getAll with
multiple keys, you can expect performance improvements of up to 8x on common
workloads.
Lower memory usage on large datasets
We’ve also significantly reduced the memory overhead incurred when working with large datasets that are too big to fit in memory. The memory overhead in these cases has been reduced by over 50%. New tables will automatically benefit from this improvement.
Improved index construction
RethinkDB 2.2 dramatically reduces the performance impact of creating a new secondary index. We’ve redesigned the index construction process to run at background priority, and to use less memory while running on a production system. Additionally, you can now restart your servers in the middle of an index construction and it will resume where it left off.
New ReQL commands
While most of the work in the 2.2 release was focused on atomic changefeeds and performance improvements on high-scale workloads, we’ve also added new ReQL commands that should make using RethinkDB more convenient.
In RethinkDB 2.2 we added a new values command that mirrors the existing
keys command and allows getting field values from an object:
// Returns `[1, 2]`
r.expr({ a: 1, b: 2}).values()
Peter Hollows expanded the r.uuid command to support
name-based UUIDs using SHA1. You can now call r.uuid(name) in
ReQL to get a name-based UUID.
We’ve also added a way for clients to determine which RethinkDB
server they’re connected to. You can call conn.server to get the server
information on a connection.
Now on Slack
We’re also really excited about the Slack group for the RethinkDB dev community. We launched the group a month ago as an experiment, and it’s growing quickly and has become an indispensable part of the community.
We’d love for you to join the Slack group, but if that’s not your cup of tea don’t worry – the development team is still on #rethinkdb on IRC.
Download RethinkDB 2.2 today
For more details check out the official release notes. To try the new release for yourself, download and install it today.
- Download RethinkDB 2.2
- Reach us on Twitter
- Start a thread in our Google Group
- Join us in the #rethinkdb channel on Freenode
- Read the
includeInitialdocumentation
Special thanks to all the amazing contributors, users, and community members who helped improve the 2.2 release!
 Ryan Paul
Ryan Paul