RethinkDB compared to MongoDB
Interested in a less biased overview? Browse through the technical comparison tables between RethinkDB and MongoDB.
Many people have been asking how RethinkDB differs from MongoDB and other NoSQL systems. Our first attempt to address these questions is a high level technical overview comparing RethinkDB with MongoDB. However, the overview is meant to be impartial, and it omits some of the more interesting bits about what makes RethinkDB special (such as our irrational love for Dota). In this post we wanted to describe the product from a more personal perspective.
In this article

The best of both worlds
First generation NoSQL products fall into roughly two categories—developer-oriented and operations-oriented.
Developer-oriented products include MongoDB and CouchDB. They typically pay close attention to ease of use, have rich document structure, and offer flexible querying capabilities. However, when compared with their operations-oriented counterparts, they are more difficult to deploy to sharded environments and to scale to significant load.
Operations-oriented systems include Cassandra and Riak. These products are designed for highly available deployments and high scale. Unlike developer-oriented products, in their current form operations-oriented products typically have less powerful querying capabilities, and tend to focus less on ease of use.
With the benefit of hindsight and three years of engineering effort, RethinkDB aims to embody ideas from each philosophy to offer the best of both worlds. It is designed to be very easy to use, has a rich data model, and supports extremely flexible querying capabilities. A cluster of RethinkDB nodes can be sharded in only a couple of clicks (really, it’s that easy, check out the screencast). Browse through the ReQL API reference to see how RethinkDB attempts to accomplish these goals.
Will Larson said it best on his blog, Irrational Exuberance:
RethinkDB has captured some of the best ideas from Cassandra and CouchDB. - Reflection on RethinkDB
Raising the bar
We’re also working on extending what’s possible with NoSQL systems. RethinkDB adds a modern query language, a massively parallel distributed infrastructure, support for distributed joins and subqueries, and has administration tools that are both simple and beautiful. Here are some of the reasons our early adopters have been especially excited about RethinkDB.
Modern query language
@rethinkdb has the best query language of all new databases that I’ve seen. - @rauchg
- ReQL is a data-driven, abstract, polymorphic query language. It’s easy to learn and extremely flexible.
- Each host language driver (currently Python, Ruby, Java, and JavaScript) implements a custom, tightly integrated domain-specific language. It’s both pragmatic and fun to use.
- Unlike most NoSQL systems, RethinkDB supports server-side subqueries and distributed join operations. This eliminates complex client-side code and multiple network roundtrips to the database server.
- ReQL is not based on string parsing, so the risk of injection attacks is greatly minimized.
That’s not to say that ReQL is complete. There are more features and operations that we’re constantly adding to the query language.
Administration: simple and beautiful
WOW. @RethinkDB’s admin interface is incredible. And installing on OSX is a cinch. Check it out people! - @mjackson
- Sharding and replication can be done in a few clicks.
- All cluster operations are scriptable in ReQL.
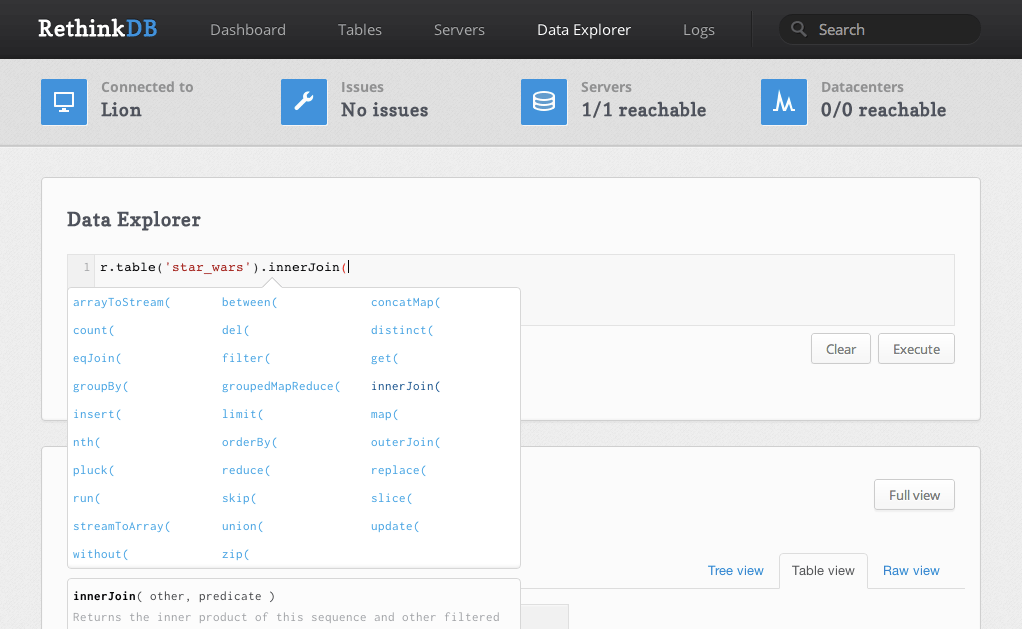
- The built-in data explorer offers online documentation and query language suggestions.
Many products are easy to use, but we think RethinkDB is beautiful. See the screencast video and be the judge yourself.
Massively parallelized distributed infrastructure
wow joins across shards, this is distributed data dream come true - @kapso
- All queries including joins, aggregation, and subqueries are automatically compiled to distributed programs and executed across the cluster without any effort from the user.
- Data intensive operations are automatically compiled to map-reduce jobs that take advantage of the distributed architecture.
- Cluster protocol is peer-to-peer and doesn’t require coordinator nodes. This makes clusters extremely easy to set up and operate.
Of course we’re always improving performance and are always working to remove more performance and scalability bottlenecks.
Robust implementation
RethinkDB looks like a MongoDB done right: MVCC, non blocking writes, durability by default, v8, incremental vacuum, easy sharding, … - @herodiade
- A lock-free architecture and a multi-version concurrency control system allow different workloads to coexist in one cluster.
- A custom, B-Tree aware buffer cache efficiently operates on datasets much larger than the amount of available RAM.
- An asynchronous, event-driven architecture based on highly optimized coroutine code scales across multiple cores and processors, network cards, and storage systems.
- A custom log-structured storage engine with a concurrent, incremental on-disk garbage compactor takes advantage of different types of storage hardware.
Limitations
RethinkDB works really well for many projects, but is not a good choice for every task. Learn more about when RethinkDB isn’t a good choice for your application.
What’s next
Form your own opinion! Take RethinkDB for a spin and don’t forget to give us your feedback so we can work out the quirks faster.
Dive into RethinkDB with the thirty-second quickstart! →